Harbour.Space Scholarship Contest 2023-2024 (Div. 1 + Div. 2) A-E 二进制拆分 组合数学
A.Increasing and Decreasing
制造一个序列,序列从 开始,到 结束,一共 个数。满足
- 序列是严格递增的
- 序列相邻两项的值是严格递减的
构造 *579
直接从 开始构造一个倒序构造一个递减序列,使每次减少的值在不重复的情况下尽可能小
void solve(){ int x, y, n; read(x, y, n);
std::vector<int> d(n); d[n-1] = y; for(int i = 2; i <= d.size(); i++){ d[d.size() - i] = d[d.size() - i + 1] - (i - 1); } if(x > d[0]){ std::cout << -1; return; } std::cout << x; for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) std::cout << " " << d[i];}B. Swap and Reverse
有一个长度为 的字符串 ,可以进行以下任一操作无限次:
- 交换相隔一位的字符,即交换 和 的字符
- 反转一段长度为 的区间
输出通过上述操作所能获得的最小字典序的字符串
思维 *1067
如果只考虑操作 1,那么我们可以将字符串的奇数位和偶数位上字符分别排序
如果使整个字符串的字典序最小,只需要判断能否将奇数位上的字符和偶数位上的自符交换位置即可。
判断 的奇偶性,当 为奇数时无法通过反转来将奇数位上的字符和偶数位上的自符交换位置,那么答案为对原字符串奇数位上的字符和偶数位上的字符分别排序。当 为偶数时,将整个字符串进行排序即可。
void solve() { int n, k; std::cin >> n >> k; std::string line; std::cin >> line;
if (k % 2 == 0) { std::sort(all(line)); std::cout << line; } else { std::string o, e; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (i % 2 == 0) o += line[i]; else e += line[i]; } std::sort(all(o)); std::sort(all(e)); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (i % 2 == 0) std::cout << o[i / 2]; else std::cout << e[i / 2]; } }}C. Divisor Chain
给一个数 ,通过下列操作将 变为
- 选择一个数 满足 是 的因数,令
注意不能使用同一个 多于两次
输出操作中的中间过程
二进制拆分 *1294
开始对着最大质因数想了至少1小时
因为 x 的 lowbit 总是 x 的因数,且二进制中的每一位只需要操作一次,所以可以
-
当 ,令
-
当 ,令 ,直到
import Data.Bitsimport Control.Monad
lowbit :: Integer -> Integerlowbit x = (.&.) (-x) x
calc :: Integer -> [Integer]calc 1 = [1]calc x | lowbit x == x = x : (calc $ x `div` 2) | otherwise = x : (calc $ x - lowbit x)
solve x = (putStrLn $ show $ length ans) >> (putStrLn $ unwords $ map show $ calc x) where ans = calc x
main :: IO()main = (read <$> getLine) >>= (flip replicateM_ $ ((read <$> getLine) >>= solve))D. Matrix Cascade
有一个大小为 的01矩阵。将矩阵中所有的元素变为 0。每次操作可以将 和 中的元素反转
输入一个矩阵,问最小需要操作几次才能将矩阵变为全
二维差分 1620
如果要反转某个位置,那么反转的区间就是从这个点开始向下的三角形
最小操作次数的解肯定是唯一的,求解的重点在于如何快速去操作这个三角形
记原来的矩阵是 ,之前的操作对 的影响为
遍历每个点 ,对每个点都需要判断:
-
如果 ,则说明之前有个反转操作对 有影响,需要将 进行反转
-
如果现在 ,则我们还说明需要进行一次反转
之后需要判断当前位置对之后的影响
-
如果当前位置 存在影响()时
-
当 时,由于需要进行一次反转使 ,因此也会使
-
当 时,保持不边,仍为
-
-
如果当前位置 不存在影响 () 时
- 当 时,由于需要进行一次反转使 ,因此
- 当 时, 保持不变
很容易发现这可以通过
然后下传标记,当 时需要下传标记。如果直接传递影响可能会难以统计,可以采用传递影响和直接操作两种方式
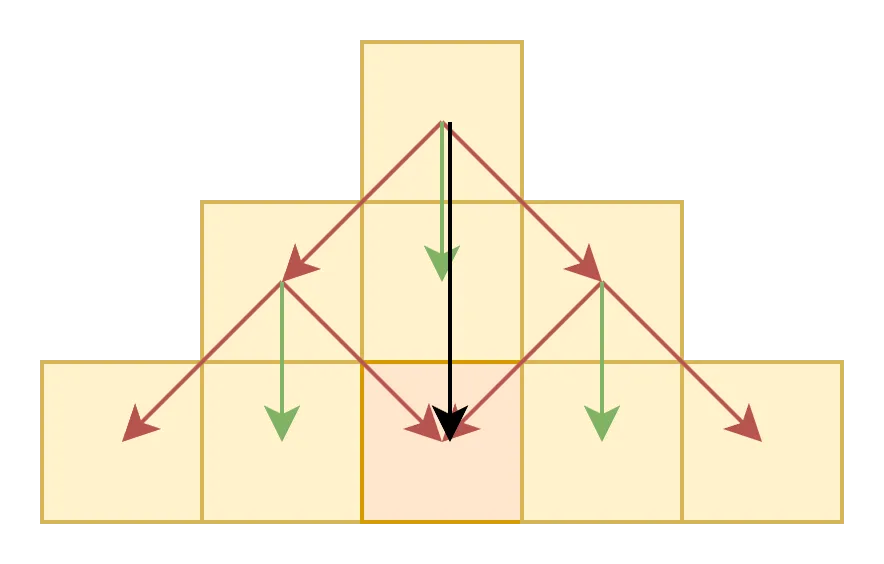
因为只有影响向下传递,而操作并不会,这样简化了传递时的操作
需要注意,像上图中橙色部分会被左右两个各传递一次,因此我们还需要再进行一次传递(黑色箭头),使变成奇数次操作
另外像下图情况
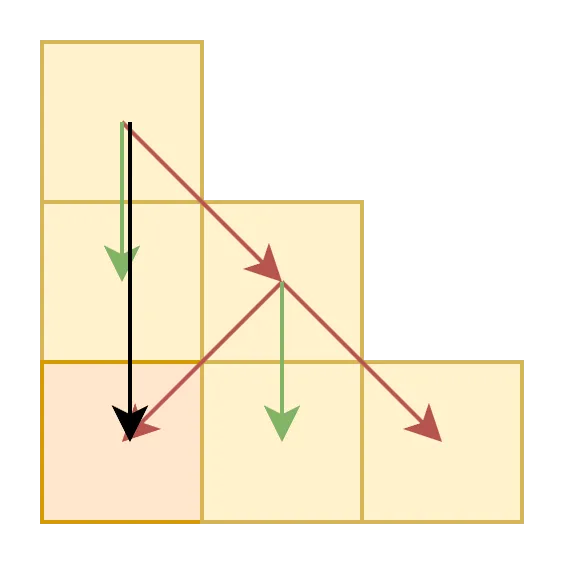
如果有黑色箭头的传递,那么橙色部分被更新了 2 次,所以还需要判断如果当前 位置,如果 或者 超过了边界,就不需要用黑色箭头对橙色块进行传递(或者再进行一次传递抵消掉)
void solve() { int n; read(n); V<V<int>> a(n + 1, V<int>(n + 1)), b(n + 1, V<int>(n + 1)); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { char ch; std::cin >> ch; a[i][j] = ch - '0'; } } int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { a[i][j] ^= b[i][j]; ans += a[i][j]; b[i][j] ^= a[i][j];
a[i][j] ^= b[i][j]; if (i + 1 < n) { a[i + 1][j] ^= b[i][j]; if (j - 1 >= 0) { b[i + 1][j - 1] ^= b[i][j]; } else if (i + 2 < n) { b[i + 2][j] ^= b[i][j]; } if (j + 1 < n) { b[i + 1][j + 1] ^= b[i][j]; } else if (i + 2 < n) { b[i + 2][j] ^= b[i][j]; } if (i + 2 < n) { b[i + 2][j] ^= b[i][j]; } } } } std::cout << ans;}E. Guess Game
Carol 有一个由非负整数组成的序列 ,她要和 Alice 和 Bob 玩 Guess Game
在游戏中,Carol 将随机选两个下标 和 ,并令 , , 和 可能重合
Carol 将:
- 告诉 Alice 的值
- 告诉 Bob 的值
- 告诉 Alice 和 Bob 的值,其中
|是位或运算Carol 不会告诉 Alice 和 Bob 任何有关 的信息
游戏开始后,Alice 和 Bob 轮流进行猜测。Alice 先手。他们的目标都是找到 或 公式哪个是正确的
在每轮猜测中,每个玩家可以进行以下一种操作:
- 回答
不知道,然后下一个玩家继续游戏- 回答
知道, 并给出游戏的答案(a<b,a>b或者a=b),游戏结束Alice 和 Bob 都能听到对方的回答,并根据回答作出自己的判断。Alice 和 Bob 足够聪明,且只会在完全确定答案的时候回答
知道要求计算游戏所进行回合数的期望值,输出答案对
998244353取模
*2113 二进制拆分 分治
很奇妙的一道题
先来看样例的几种情况
| 11 | 11 | 10 |
| IDK | ||
| A 的最高位是 ,B 的最高位也是 。第二位小,所以 |
| 11 | 11 | 11 |
| IDK | ||
| A 的最高位是 ,B 的最高位也是 。B 的次高位仍是 ,不能判断大小关系, IDK | ||
| B 的最高位和次高位都是 ,因此 |
也就是说如果先手具有最高位,它就无法判断大小关系(因为他无法判断对方最高位是否为 ),这时候先手回答 不知道。后手如果这一位是 0,则大小关系可判断。如果这一位是1,可以先把先手和后手的最高位都删掉,交换先后手重新判断。
这样我们就获得一个 的计算轮数的方式
unsigned int highbit(unsigned int x) { return (1u << (31 - __builtin_clz(x))); }int pk(int a, int b, int round = 1) { int x = a | b; if (a == 0) return round; if (highbit(a) != highbit(x)) return round; if (b == 0) return round + 1; if (highbit(b) != highbit(x)) return round + 1; return pk(b & (highbit(x) - 1), a & (highbit(x) - 1), round + 1);}但是如果要判断一个序列中轮数的期望,仍然需要 次判断,对于这个题是数据范围来说是 Unacceptable 的,因此还需要从数据特征进一步分析
因为轮数和两个数的高位有关,可以考虑将这个序列根据最高位的位置分为 31 ,同一组中最高位的位置相同。
-
对于不同组之间选两个数,那么他们由于最高位不同,只需要 轮即可结束(高位先手和低位先手)。对于所有元素来说就是 轮
-
对于同一组中选两个数,由于最高位相同,所以需要去掉最高位再进行判断。可以根据次高位的位置,重新将其分组,并计算选择不同组和同组的轮数进行相加,直到一组中全为 0
#pragma GCC optimize(2)// clang-format off#include <bits/stdc++.h>using i16 = short; using i32 = int; using i64 = long long; using u16= unsigned short; using u32 = unsigned int; using u64 = unsigned long long;using f32 = float; using f64 = double; using f128 = long double;using pii = std::pair<i32, i32>; using pll = std::pair<i64, i64>; using pil = std::pair<i32, i64>; using pli = std::pair<i64, i32>;template<class T> using V = std::vector<T>;template <typename T> inline typename std::enable_if<std::is_integral<T>::value>::type read(T &x){ char c;T f=1; while(!isdigit(c=getchar())) if(c=='-')f=-1; x=(c&15); while(isdigit(c=getchar())) x= (x<<1) + (x<<3) + (c&15); x*=f; } template <typename T, typename... A> inline void read(T &value, A &..._t) { read(value), read(_t...); } template <typename T> inline void reads(T begin, T end){ while(begin != end) { read(*begin); begin++; } }void solve(); void init();int TESTCASE = 1; int main() { init(); for(int i = 1; i <= TESTCASE; i++){ solve(); if(i != TESTCASE) std::cout << "\n"; } return 0;}template<class T> T fstTrue(T l, T r, std::function<bool(T)> check){ assert(l <= r); while(l < r){ T mid = l + (r - l) / 2; if(check(mid)) r = mid; else l = mid + 1; } return r; }template<class T> T lstTrue(T l, T r, std::function<bool(T)> check){ assert(l <= r); while(l < r){ T mid = l + (r - l + 1)/2; if(check(mid)) l = mid; else r = mid - 1; } return l; }template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) { return std::__gcd(a, b); }template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) { return a / gcd(a, b) * b; };template<const int T> struct MInt { const static int mod = T; int x; MInt(int x = 0) : x(x % mod) {} MInt(long long x) : x(int(x % mod)) {} int val() { return x; } MInt operator + (const MInt &a) const { int x0 = x + a.x; return MInt(x0 < mod ? x0 : x0 - mod); } MInt operator - (const MInt &a) const { int x0 = x - a.x; return MInt(x0 < 0 ? x0 + mod : x0); } MInt operator * (const MInt &a) const { return MInt(1LL * x * a.x % mod); } MInt operator / (const MInt &a) const { return *this * a.inv(); } bool operator == (const MInt &a) const { return x == a.x; }; bool operator != (const MInt &a) const { return x != a.x; }; void operator += (const MInt &a) { x += a.x; if (x >= mod) x -= mod; } void operator -= (const MInt &a) { x -= a.x; if (x < 0) x += mod; } void operator *= (const MInt &a) { x = 1LL * x * a.x % mod; } void operator /= (const MInt &a) { *this = *this / a; } friend MInt operator + (int y, const MInt &a){ int x0 = y + a.x; return MInt(x0 < mod ? x0 : x0 - mod); } friend MInt operator - (int y, const MInt &a){ int x0 = y - a.x; return MInt(x0 < 0 ? x0 + mod : x0); } friend MInt operator * (int y, const MInt &a){ return MInt(1LL * y * a.x % mod);} friend MInt operator / (int y, const MInt &a){ return MInt(y) / a;} friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const MInt &a) { return os << a.x;} friend std::istream &operator>>(std::istream &is, MInt &t){return is >> t.x;} MInt pow(int64_t n) const { MInt res(1), mul(x); while(n){ if (n & 1) res *= mul; mul *= mul; n >>= 1; } return res; } MInt inv() const { int a = x, b = mod, u = 1, v = 0; while (b) { int t = a / b; a -= t * b; std::swap(a, b); u -= t * v; std::swap(u, v); } if (u < 0) u += mod; return u; } };#define debug(...) debug_do std::cerr << "[" << #__VA_ARGS__ << "]:", __debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)#define maxnum(type) std::numeric_limits<type>::max()#define minnum(type) std::numeric_limits<type>::min()#define pb push_back#define pf push_front#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()#define rall(x) (x).rbegin(), (x).rend()#define all1(x) ++(x).begin(), (x).end()#define rall1(x) (x).rbegin(), --(x).rend()#define rep(i, n) for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)#define rep1(i, n) for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)template<class R, class A> R mmax(R x, A y){ return std::max(x, (R) y); } template<class R, class A, class... AS> R mmax(R x, A xx, AS... xxs){ return std::max(x, mmax((R)xx, xxs...)); }template<class R, class A> R mmin(R x, A y){ return std::min(x, (R) y); } template<class R, class A, class... AS> R mmin(R x, A xx, AS... xxs){ return std::min(x, mmin((R)xx, xxs...)); }using std::cout; using std::cin; using std::endl;#define endl "\n"// clang-format on
// using i128 = __int128;void init() { read(TESTCASE); // std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); std::cin.tie(nullptr); // std::cout.tie(nullptr); std::cin >> TESTCASE;}using Z = MInt<998244353>;void solve() { int n; read(n); V<int> s(n); reads(all(s)); auto highpos = [](unsigned x) { if (x == 0) return 0; return 32 - __builtin_clz(x); }; auto highbit = [&highpos](unsigned x) { if (x == 0) return x; return 1u << (highpos(x) - 1); };
std::function<Z(V<int> &, int)> divide = [&](V<int> &seq, int round) { std::array<V<int>, 32> group; int num = seq.size(); Z ans = 0; debug(seq); for (auto i : seq) { group[highpos(i)].pb(i); }
for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) { auto g = group[i]; if (g.size() == 0) continue;
ans += (int)(g.size() * (num - g.size())) * (2 * round + 1); // 不同组之间选数
if (i != 0) { for (auto &b : g) b -= highbit(b); // 同组间选数,删除最高位 ans += divide(g, round + 1); } else { // 一组中全是 0 了,组内选数直接是 1 轮结束
ans += (int)(g.size() * g.size() * (1 * round)); }
num -= g.size(); // 防止选重复,组间选数只选择当前组和该组之后的组 } return ans; };
std::cout << (divide(s, 1) / n / n);}